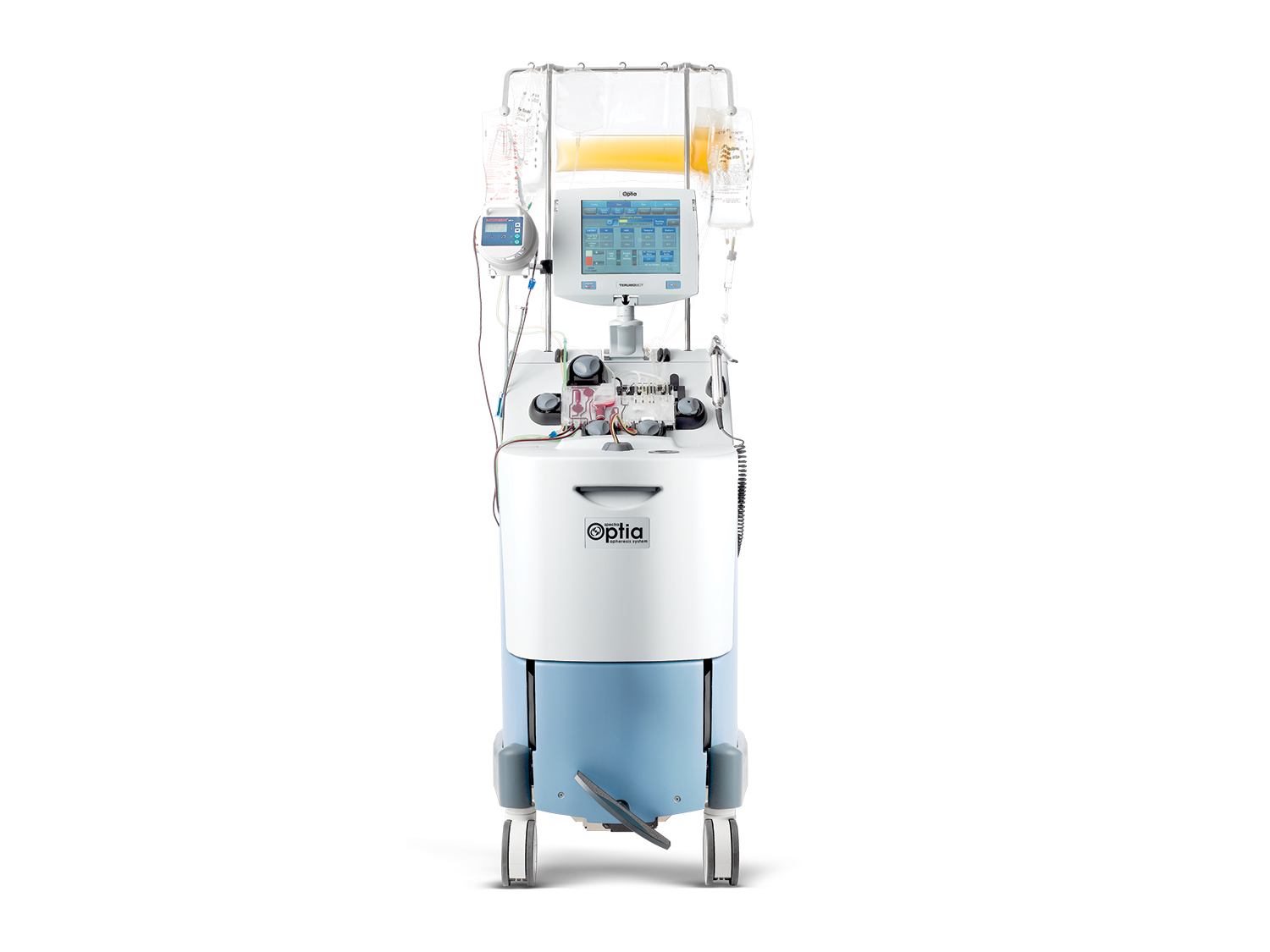
探索 RBCX 对镰状红细胞疾病 (SCD) 成人和儿童患者输血管理的价值*
鼓舞人心的患者故事
患者比任何人都更了解镰状细胞病(SCD)如何影响他们的生活。我们分享这些故事,旨在鼓舞患者和临床医生,他们每天都在努力平衡应对这种疾病的挑战。
与简单的输血和手动置换相比,RBCX 具有以下优点:
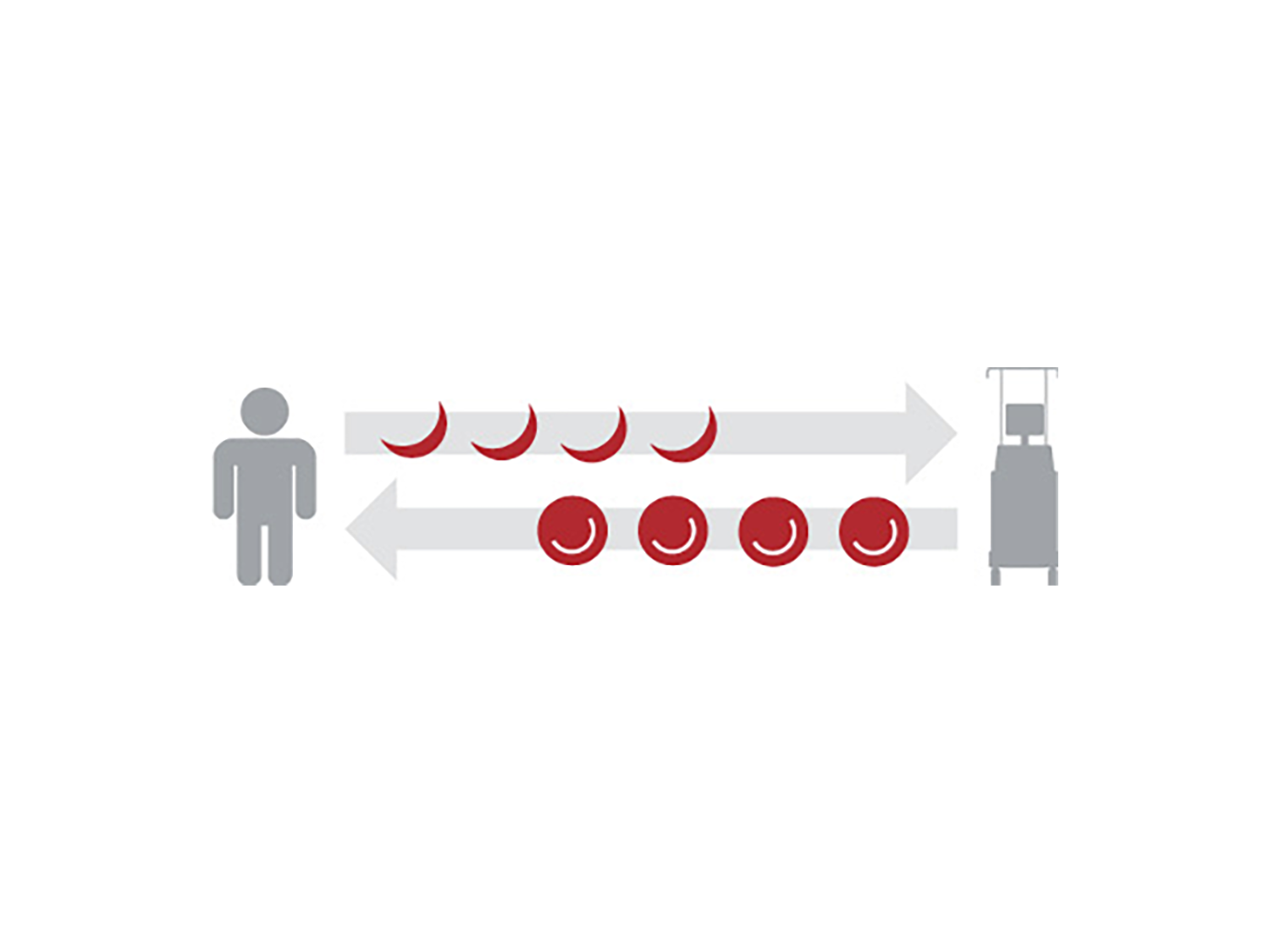
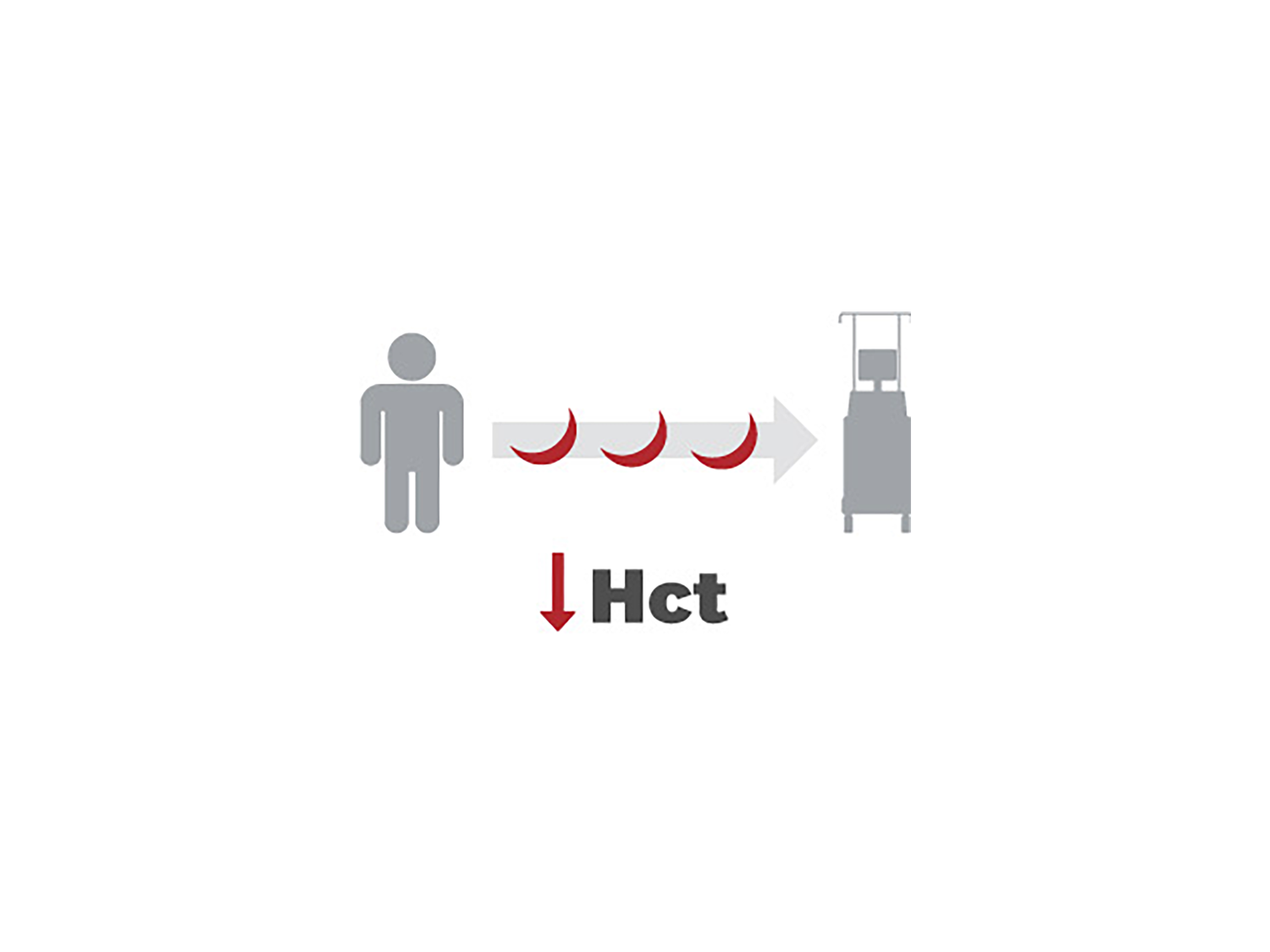
- 去除含有血红蛋白 S (HbS) 的红细胞 (RBC) 并快速替换为健康红细胞,同时维持等血容量1-5
- 管理铁过剩和血液粘度1,4,7
- 控制 HbS 和血细胞比容3-4,6,8-9
"与其他输血疗法相比,我发现 RBC 置换是维持血红蛋白 S 低百分比并将铁负荷降至最低程度的更有效方法。"
Julie Kanter, 医学博士
镰状细胞研究部主任
南卡罗来纳州医科大学
资料
- 文件
- 链接
了解更多关于红细胞置换的信息。
禁忌证
- 除了与所有自动化血液分离系统相关的禁忌证之外,尚不清楚使用本系统会带来哪些禁忌证
- 有些病人可能有输注某些溶液和替换液的禁忌
病人可能出现的反应
- 焦虑、头痛、头晕、手指和/或面部感觉异常、发烧、寒战、血肿、过度换气、恶心和呕吐、晕厥、荨麻疹、低血压和过敏反应
输血反应包括10
- 发烧、循环超负荷、休克、过敏反应、同种异体免疫、移植物抗宿主病和感染传播
仅限处方使用
- 操作员必须熟悉系统的操作说明
- 程序必须由合格的医务人员执行
- 监督医生可以在医院办公室或不属于医院正式部分的其他非医院空间进行监督,但前提是监督医生可以立即赶到现场.11
免责声明和备注
*在不同的国家其可用的产品和程序会有差异。
- Adams D, et al, Erythrocytapheresis can reduce iron overload and prevent the need for chelation therapy in chronically transfused pediatric patients. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1996;18(1):46-50.
- Danielson C, et al. The role of red blood cell exchange transfusion in the treatment and prevention of complications of sickle cell disease. Ther Apher. 2002;6(1):24-31.
- Wahl S, et al. Lower alloimmunization rates in pediatric sickle cell patients on chronic erythrocytapheresis compared to chronic simple transfusions. Transfusion. 2012;52(12):2671-2676.
- Lawson SE, et al. Red cell exchange in sickle cell disease. Clin Laboratory Haemotol. 1999;21(2):99-102.
- Wayne S, et al. Transfusion management of sickle cell disease. Blood. 1993;81(5):1109-1123.
- Cabibbo S, et al. Chronic RBC exchange to prevent clinical complications in sickle cell disease. Transfus Apher Sci. 2005;32(3):315-321.
- Hilliard L, et al. Erythrocytapheresis limits iron accumulation in chronically transfused SCD patients. Amer J Hematol. 1998;59(1):28-35.
- Duclos C, et al. Long-term red blood cell exchange in children with sickle cell disease: Manual or automatic? Transfus Apher Sci. 2013;48(2):219-222.
- Singer S, et al. Erythrocytapheresis for chronically transfused children with sickle cell disease: An effective method for maintaining a low HbS level and reducing iron overload. J Clin Apher. 1999;14(3):122-125.
- AABB (ed.), et al. Circular of Information for the Use of Human Blood and Blood Components. 10th ed. Seattle, WA. Council of Europe Publishing,
- American Society for Apheresis. Guidelines for documentation of therapeutic apheresis procedures in the medical record by apheresis physicians. J Clin Apher. 2007;22(3):183.